Molecular
Diagnostics and Genotyping
CHD is happy to add an aspect of molecular diagnostics to its repertoire
of services. Following published manuscripts, Cryptosporidium spp.1,2
and Giardia lamblia3 can be detected via the polymerase
chain reaction (PCR) in treated, raw, and waste waters. In addition, speciation,
lineage, and/or genotype determination are accomplished using restriction
fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) and DNA sequencing.
Figure: 1.5% EtBr stained agarose gel depicting Cryptosporidium
species determination via RFLP digestion of a PCR amplified segment within the
18S rRNA gene.
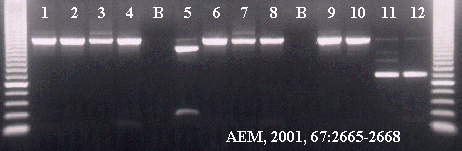
Lane L: 50Bp Marker
Lane
1: C. hominis PCR amplified product size: 593bp
Lane 2: C. parvum
PCR amplified product size 590bp
Lane 3: C.
baileyi PCR amplified product size 579bp
Lane 4: C.
serpentis PCR amplified product size 583bp
B: Blank
Lane 5: C. hominis
amplified product digested with VspI enzyme
Lane 6: C. parvum
amplified product digested with VspI enzyme
Lane 7: C.
baileyi amplified product digested with VspI enzyme
Lane 8: C.
serpentis amplified product digested with VspI enzyme
B: Blank
Lane 9: C. hominis
amplified product digested with DraII enzyme
Lane 10: C. parvum
amplified product digested with DraII enzyme
Lane 11: C. baileyi amplified
product digested with DraII enzyme
Lane 12: C. serpentis amplified
product digested with DraII enzyme
Figure 2: 0.8% EtBr stained agarose gel depicting an approximate 500bp size
polymorphism within the GP900 surface protein gene noted between C. parvum and
C. hominis.
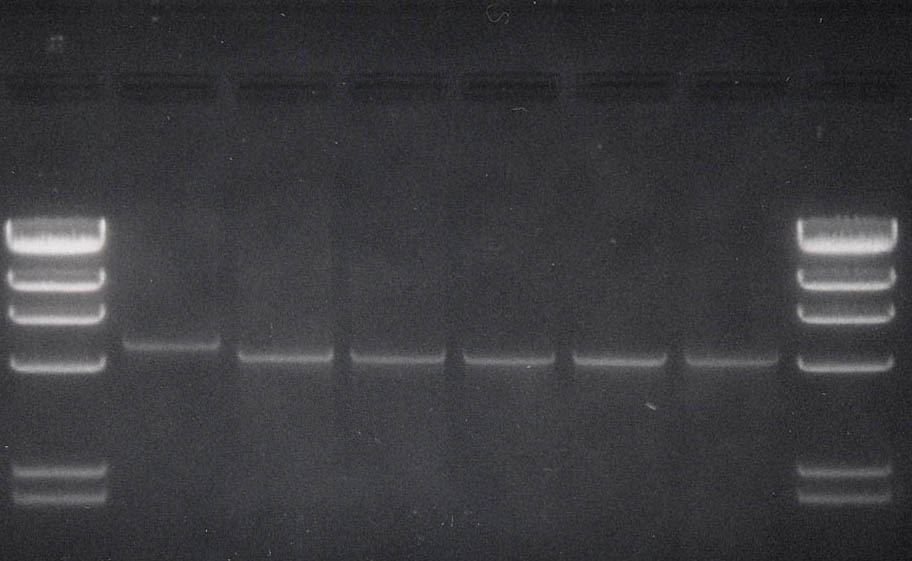
Lane L: Marker, Lambda DNA digested with HindIII
Lane 1: C. parvum, Iowa Isolate (a.k.a. genotype II); Band Size: ~ 5100bp
Lane 2: C. hominis, Peruvian Isolate 278 (a.k.a. genotype I)
Lane 3: C. hominis, Peruvian Isolate 339 (a.k.a. genotype I)
Lane 4: C. hominis, Peruvian Isolate JOJ (a.k.a. genotype I)
Lane 5: C. hominis, Peruvian Isolate (a.k.a. genotype I)
Lane 6: C. hominis, Peruvian Isolate (a.k.a. genotype I)
Peruvian isolates donated by Dr. Robert Gilman,
Johns Hopkins University
USA isolates donated by Dr. Michael Arrowood, C.D.C
1 Sturbaum, GD,
C Reed, PJ Hoover, BH Jost, MM Marshall, and CR Sterling. 2001.
Species-Specific, Nested PCR-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Detection
of Single Cryptosporidium parvum Oocysts.
Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 67:2665-2668.
2 Gobet
P, Toze S. Sensitive genotyping of Cryptosporidium
parvum by PCR-RFLP analysis of the 70-kilodalton heat shock protein (HSP70)
gene. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2001;200:37-41.
3 Hopkins RM, Meloni BP, Groth DM, Wetherall JD,
Reynoldson JA, Thompson RC.
Ribosomal RNA sequencing reveals differences between the genotypes of Giardia
isolates recovered from humans and dogs living in the same locality.
Journal of Parasitology. 1997 Feb;83(1):44-51.
4 Lu SQ, Baruch AC, Adam RD. Molecular comparison
of Giardia lamblia isolates. International Journal for Parasitology. 1998
Sep;28(9):1341-5.
|